
Non Destructive Testing, Thermography and Flash Strobe
Phoxene, strobe photography
For over 25 years, Phoxene has acquired know-how in the technical design, manufacture and sale of flash solutions for various industrial applications, including thermography and non-destructive testing. Phoxene has delivered thousands of flash devices to system integrators worldwide.
NON DESTRUCTIVE TESTING
Nondestructive testing or non-destructive testing (NDT) is a wide group of analysis techniques used in science and technology industry to evaluate the properties of a material, component or system without causing damage.
Among all the analysis techniques used by non-destructive testing, a few ones use short pulses of light or radiation in the Near Infra-Red region, such as the ones produced by Xenon flash sources.
FLUORESCENCE ANALYSIS
This technique of fluorescence analysis, or fluorescence spectroscopy, involves a beam of light that excites the electrons in molecules of a sample, and causes them to re-emit light with a different wavelength. This re-emitted light is analyzed to reveal properties of the sample.
A variant of this technique is used for a direct count of fluorescent microorganisms: their count is proportional to the amount of light obtained by fluorescence.
Fluorescence analysis demands a well-defined and stable light source in terms of light output and spectrum. This is exactly the type of light produced by a xenon flash.
THERMOGRAPHY
The most widely used, active mode NDT method is flash thermography, in which the surface of the test piece is heated by a light pulse lasting only a few milliseconds. Under normal conditions, the part cools after flash heating, as the heat deposited at the surface flows toward the cooler interior. However, internal anomalies in the test piece, such as voids, inclusions, delamination, moisture, or changes in thickness or density, cause changes in the cooling rate at the surface.
WHY A XENON FLASH FOR NON-DESTRUCTIVE TESTING
Xenon flashes do offer a wide spectrum rich in visible light and near infrared, and they deliver their radiation under a very high power in the range of hundreds of kiloWatt. Furthermore their short pulses in the range of the millisecond make xenon flashes remarkable light sources for non-destructive testing.
Xenon Flash spectrum
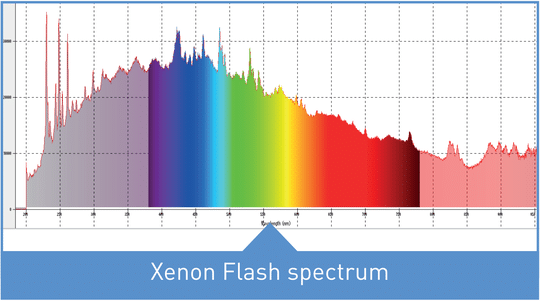
The spectrum produced by xenon flash sources is rich in visible and IR emission. UV is usually filtered-out by the glass wall itself, but can be enhanced for some applications.
In the visible band, the Xenon Flash spectrum is close to that of a blackbody radiator at 6000K.
Furthermore, this spectrum is very stable and repeatable.
High Energy and high power
A xenon flash strobe operates in two separate sequences:
- – a “charge” where energy is stored from an electrical supply into storage capacitors, in a matter of seconds. This is a low power process, involving a few Watts of electrical supply.
- – a “discharge” where the energy stored in the capacitors is brutally released and converted into radiations by a xenon flash lamp, under the form of a spectrum centered on visible light.
This discharge process being very fast, it occurs under a very high power typically on the order of 100.000 Watts.

PHOXENE FLASH SOLUTIONS FOR NDT AND THERMOGRAPHY
As a manufacturer, Phoxene offers a range of readily available illuminators, as well as custom-designed solutions for non-destructive testing and thermography, including features such as:
- – Long pulses or short pulses
- – Individual flashes, bursts of flashes, or stroboscopic output
- – A variety of power and energy levels
- – Narrow or wide beam angles





